Mybatis
Hello Mybatis
配置环境
配置maven项目的pom.xml文件
配置依赖
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14<dependencies>
<!-- MyBatis依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.22</version>
</dependency>
<!-- mysql数据库连接依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.5.6</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>对于mapper的xml文件找不到问题,需在pom.xml文件中声明下述代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21<!--在build中配置resources,来防止我们资源导出失败的问题-->
<build>
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/resources</directory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.properties</include>
<include>**/*.xml</include>
</includes>
<filtering>true</filtering>
</resource>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/java</directory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.properties</include>
<include>**/*.xml</include>
</includes>
<filtering>true</filtering>
</resource>
</resources>
</build>
创建MyBatis主配置文件
1 |
|
遇到问题:
Cause: com.sun.org.apache.xerces.internal.impl.io.MalformedByteSequenceException: 2 字节的 UTF-8 序列的字节 2 无效;错误原因暂不明;
解决方法:
删去注释;
在pom文件中加入下面代码或
1
2
3<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
</properties>
Cause: org.xml.sax.SAXParseException; lineNumber: 1; columnNumber: 1; 前言中不允许有内容;错误原因:mybatis主配置文件编码问题
创建MyBatisUtils工具类
1 | public class MybatisUtils { |
编写Mapper接口及xml文件
1 | public interface StudentDao { |
1 |
|
编写测试类
1 | public class MyTest { |
Mybatis的一些重要对象
Resource:负责读取主配置文件SqlSessionFactoryBuilder:负责创建SqlSessionFactory对象
1 | //基础配置代码 |
SqlSessionFactory:用于获取SqlSession对象特点:
创建的对象是一个重量级对象:创建此对象需要使用更多的资源和时间
1
官方文档说明:SqlSessionFactory 一旦被创建就应该在应用的运行期间一直存在,没有任何理由丢弃它或重新创建另一个实例。 使用 SqlSessionFactory 的最佳实践是在应用运行期间不要重复创建多次,多次重建 SqlSessionFactory 被视为一种代码“坏习惯”。因此 SqlSessionFactory 的最佳作用域是应用作用域。 有很多方法可以做到,最简单的就是使用单例模式或者静态单例模式。
是一个接口:是
SqlSession的工厂类,用于创建SqlSession对象,DefaultSqlSessionFactory是其实现类1
public class DefaultSqlSessionFactory implements SqlSessionFactory
常用方法:
1
2
3
4
5//获取一个默认的SQLSession对象,默认手动提交事务
SqlSession openSession();
//在上述基础上控制是否自动提交事务
SqlSession openSession(boolean autoCommit);
SqlSession:由SqlSessionFactory对象获取得到,本身为一个接口1
2//实现类
public class DefaultSqlSession implements SqlSession作用:提供了大量的执行sql语句的方法:
1
2
3selectOne:执行sql查询语句,得到最多一行记录,多余1行则报错
selectList:执行sql查询语句,返回多条记录
insert/update/delete/commit/rollback:同sql语句注:线程不安全,使用步骤:
- 在方法内部使用sql前先获取
SqlSession对象 - 调用
SqlSession的方法执行sql语句 - 关闭
SqlSession
- 在方法内部使用sql前先获取
使用动态代理简化
如果我们要使用MyBatis进行数据库操作的话,大致要做两件事情:
- 定义dao接口文件:在dao接口中定义需要进行的数据库操作方法;
- 创建映射文件:当有了dao接口后,还需要为该接口创建映射文件,映射文件中定义了一系列SQL语句,这些SQL语句和dao接口一一对应;
MyBatis在初始化的时候会将映射文件与dao接口一一对应,并根据映射文件的内容为每个函数创建相应的数据库操作能力。而我们作为MyBatis使用者,只需将dao接口注入给Service层使用即可。
那么MyBatis是如何根据映射文件为每个dao接口创建具体实现的?答案是——动态代理。
1 | StudentDao dao = session.getMapper(StudentDao.class); //Mybatis通过代理生成dao接口的实现类 |
用法:
1 | //使用代理技术完成简单使用Mybatis |
占位符
#占位符,推荐使用。语法:
#{字符}Mybatis处理
#{字符}使用的是jdbc的PrepareStatment对象。特点:
- 执行sql语句效率高;
- 保证安全性,防注入;
- 常常作为列值使用,位于等号的右侧,其值和数据类型相关。
$占位符,使用基本与#占位符相同语法:
${字符}Mybatis处理
${字符}使用的是jdbc的Statment对象。常常作为表名或列名使用,在能保证数据安全的情况下使用该占位符。
使用地方:如
order排序时
MyBatis配置
1、mybatis-config.xml,MyBatis核心配置文件
注意不同标签插入的顺序有要求,必须依照下述顺序
1 | (properties?, settings?, typeAliases?, typeHandlers?, objectFactory?, objectWrapperFactory?, |
1)properties(属性),引入外部配置文件
1 | driver = com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver |
1 | <properties resource="db.properties"/> |
注:对于外部引入properties属性与配置文件中自定义属性同名的,外部引入的属性优先级更高,优先使用外部引入属性。
2)typeAliases(类型别名)
类型别名可为 Java 类型设置一个缩写名字。 它仅用于 XML 配置,意在降低冗余的全限定类名书写。
1
2
3<typeAliases>
<typeAlias alias="Author" type="domain.blog.Author"/>
</typeAliases>当这样配置时,
Blog可以用在任何使用domain.blog.Blog的地方。也可以指定一个包名,MyBatis 会在包名下面搜索需要的 Java Bean,比如:
1
2
3<typeAliases>
<package name="domain.blog"/>
</typeAliases>每一个在包
domain.blog中的 Java Bean,在没有注解的情况下,会使用 Bean 的首字母小写的非限定类名来作为它的别名。 比如domain.blog.Author的别名为author;若有注解,则别名为其注解值。见下面的例子:1
2
3
public class Author {
}
4)设置(settings)
| 设置名 | 描述 | 有效值 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|---|
mapUnderscoreToCamelCase |
是否开启驼峰命名自动映射,即从经典数据库列名A_COLUMN映射到经典Java属性名aColumn |
true |
false |
logImpl |
指定MyBatis所用日志的具体实现,未指定时将自动查找。 | LOG4J |
STDOUT_LOGGING |
cacheEnabled |
全局性地开启或关闭所有映射器配置文件中已配置的任何缓存。 | true |
false |
lazyLoadingEnabled |
延迟加载的全局开关。当开启时,所有关联对象都会延迟加载。 特定关联关系中可通过设置fetchType属性来覆盖该项的开关状态。 |
true |
false |
日志实现——log4j
apache开源的一个日志实现。
简单使用
在要使用Log4j 的类中,导入包
import org.apache.log4j.Logger;日志对象,参数为当前类的class
1
static Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(UserDaoTest.class);
日志级别
1
2
3logger.info("info:进入了testLog4j");
logger.debug("debug:进入了testLog4j");
logger.error("error:进入了testLog4j");
MyBatis中使用步骤:
先导入具体jar包
1
2
3
4
5<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>1.2.17</version>
</dependency>在resource目录下创建
log4j.properties配置文件1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24#将等级为DEBUG的日志信息输出到console和file这两个目的地,console和file的定义在下面的代码
=DEBUG,console,file
#控制台输出的相关设置
= org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender
= System.out
=DEBUG
= org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
=[%c]-%m%n
#文件输出的相关设置
= org.apache.log4j.RollingFileAppender
=./log/kuang.log
=10mb
=DEBUG
=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
=[%p][%d{yy-MM-dd}][%c]%m%n
#日志输出级别
=DEBUG
=DEBUG
=DEBUG
=DEBUG
=DEBUG在mybatis-config.xml主配置文件中设置日志实现未log4j
1
2
3
4<!--添加日志功能-->
<settings>
<setting name="logImpl" value="LOG4J"/>
</settings>
5)映射器(mappers)
引入Mapper文件
1 | <mappers> |
resultMap,结果集映射
用于解决实体类属性名与数据库表字段名不匹配问题。
属性的对应关系:
1 | <!-- id表示此resultMap的id,用于之后sql语句中引用,type表示Java实体类 --> |
案例:
具体解决再上述xml代码中已经说明。
- 查找学号为
95001的学生所选修的课程中成绩最高的课程。 - 查找学号为
95001的学生选修的所有课程。
动态sql
在 MyBatis 之前的版本中,需要花时间了解大量的元素。借助功能强大的基于 OGNL 的表达式,MyBatis 3 替换了之前的大部分元素,大大精简了元素种类,现在要学习的元素种类比原来的一半还要少。
ifchoose (when, otherwise)trim (where, set)foreach
if标签
1 | <select id="selectDetailInfoIf" resultMap="SCMap"> |
使用注解开发
Lombok
插件工具,用于简化简单实体类的创建。
主要使用其注解,包含如下注解:
1 | and |
使用步骤;
在IDEA中下载插件Lombok
导入对应依赖
1
2
3
4
5<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.18</version>
</dependency>在实体类中使用,作用域为类
常用注解详解:
@Data:用于生产实体类的无参构造方法、Getter/Setter方法、toString方法、hasCode方法、equals等基础方法;@RequiredArgsConstructor:创建有参构造方法;@NoArgsConstructor:创建无参构造方法;@EqualsAndHashCode、@ToString、@Getter、@Setter
缓存
简介
1 | 查询 : 连接数据库 ,耗资源! |
- 什么是缓存 [ Cache ]?
- 存在内存中的临时数据。
- 将用户经常查询的数据放在缓存(内存)中,用户去查询数据就不用从磁盘上(关系型数据库数据文件)查询,从缓存中查询,从而提高查询效率,解决了高并发系统的性能问题。
为什么使用缓存?
- 减少和数据库的交互次数,减少系统开销,提高系统效率。
什么样的数据能使用缓存?
- 经常查询并且不经常改变的数据。【可以使用缓存】
Mybatis缓存
MyBatis包含一个非常强大的查询缓存特性,它可以非常方便地定制和配置缓存。缓存可以极大的提升查询效率。
MyBatis系统中默认定义了两级缓存:一级缓存和二级缓存
默认情况下,只有一级缓存开启。(SqlSession级别的缓存,也称为本地缓存)
二级缓存需要手动开启和配置,他是基于namespace级别的缓存。
为了提高扩展性,MyBatis定义了缓存接口Cache。我们可以通过实现Cache接口来自定义二级缓存
一级缓存
- 一级缓存也叫本地缓存: SqlSession
- 与数据库同一次会话期间查询到的数据会放在本地缓存中。
- 以后如果需要获取相同的数据,直接从缓存中拿,没必须再去查询数据库;
测试步骤:
- 开启日志!
- 测试在一个Sesion中查询两次相同记录
- 查看日志输出
\Mybatis\Mybatis课堂笔记.assets\1569983650437.png)
缓存失效的情况:
查询不同的东西
增删改操作,可能会改变原来的数据,所以必定会刷新缓存!
\Mybatis\Mybatis课堂笔记.assets\1569983952321.png)
查询不同的Mapper.xml
手动清理缓存!
\Mybatis\Mybatis课堂笔记.assets\1569984008824.png)
小结:一级缓存默认是开启的,只在一次SqlSession中有效,也就是拿到连接到关闭连接这个区间段!
一级缓存就是一个Map。
二级缓存
- 二级缓存也叫全局缓存,一级缓存作用域太低了,所以诞生了二级缓存
- 基于namespace级别的缓存,一个名称空间,对应一个二级缓存;
- 工作机制
- 一个会话查询一条数据,这个数据就会被放在当前会话的一级缓存中;
- 如果当前会话关闭了,这个会话对应的一级缓存就没了;但是我们想要的是,会话关闭了,一级缓存中的数据被保存到二级缓存中;
- 新的会话查询信息,就可以从二级缓存中获取内容;
- 不同的mapper查出的数据会放在自己对应的缓存(map)中;
步骤:
开启全局缓存
1
2<!--显示的开启全局缓存-->
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>在要使用二级缓存的Mapper中开启
1
2<!--在当前Mapper.xml中使用二级缓存-->
<cache/>也可以自定义参数
1
2
3
4
5<!--在当前Mapper.xml中使用二级缓存-->
<cache eviction="FIFO"
flushInterval="60000"
size="512"
readOnly="true"/>测试
问题:我们需要将实体类序列化!否则就会报错!
1
Caused by: java.io.NotSerializableException: com.kuang.pojo.User
小结:
- 只要开启了二级缓存,在同一个Mapper下就有效
- 所有的数据都会先放在一级缓存中;
- 只有当会话提交,或者关闭的时候,才会提交到二级缓冲中!
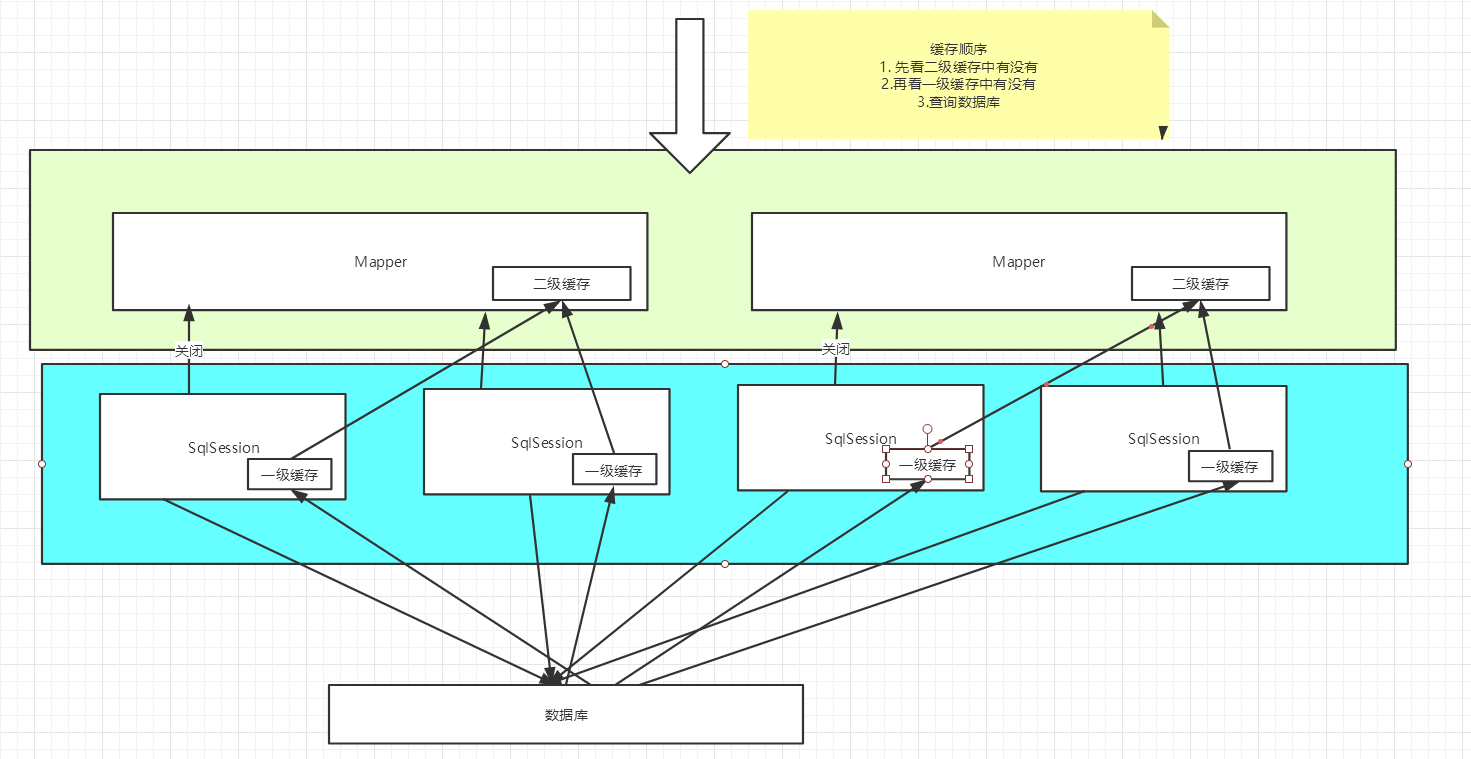
缓存原理
自定义缓存-ehcache
1 | Ehcache是一种广泛使用的开源Java分布式缓存。主要面向通用缓存 |
要在程序中使用ehcache,先要导包!
1 | <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.mybatis.caches/mybatis-ehcache --> |
在mapper中指定使用我们的ehcache缓存实现!
1 | <!--在当前Mapper.xml中使用二级缓存--> |
ehcache.xml
1 |
|
Redis数据库来做缓存! K-V
数据库环境
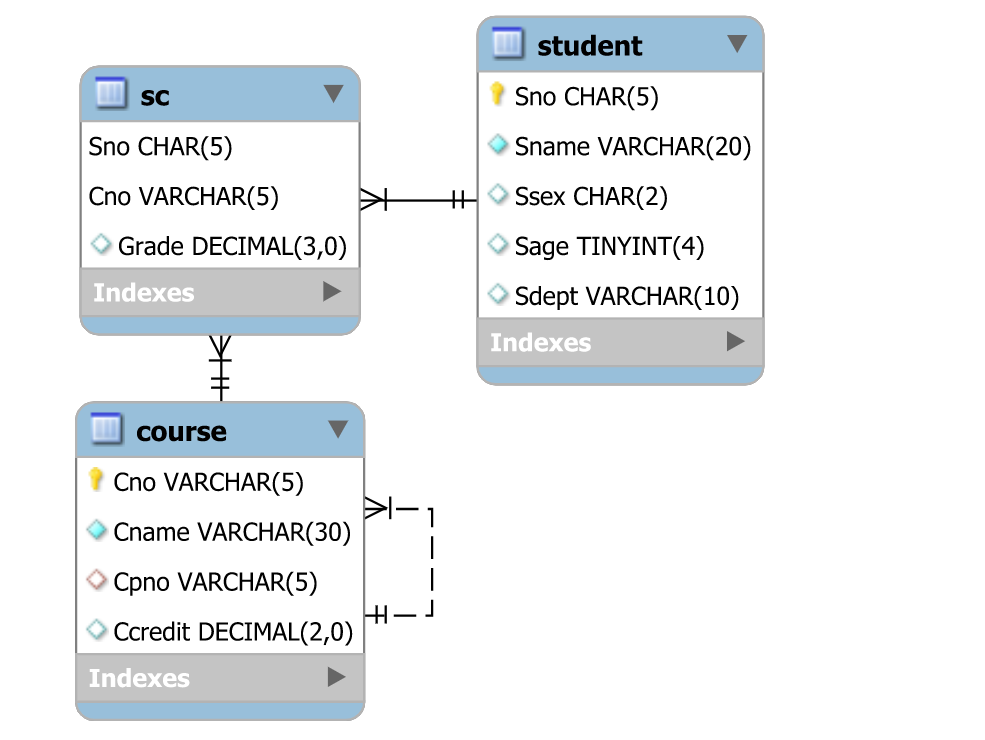
测试环境:学生选课数据库,学生表student、课程表实体表course,为多对多关系——即一门课可被多个学生选择/一个学生可选择多门课,该关系对应关系表sc,在course课程表中,存在一对多关系,每门课可以有前置课程(无前置课程Cpno为null),而一门课可为多门课的前置课程,具体ER图如下。
脚本如下:
1 | SET @OLD_UNIQUE_CHECKS=@@UNIQUE_CHECKS, UNIQUE_CHECKS=0; |